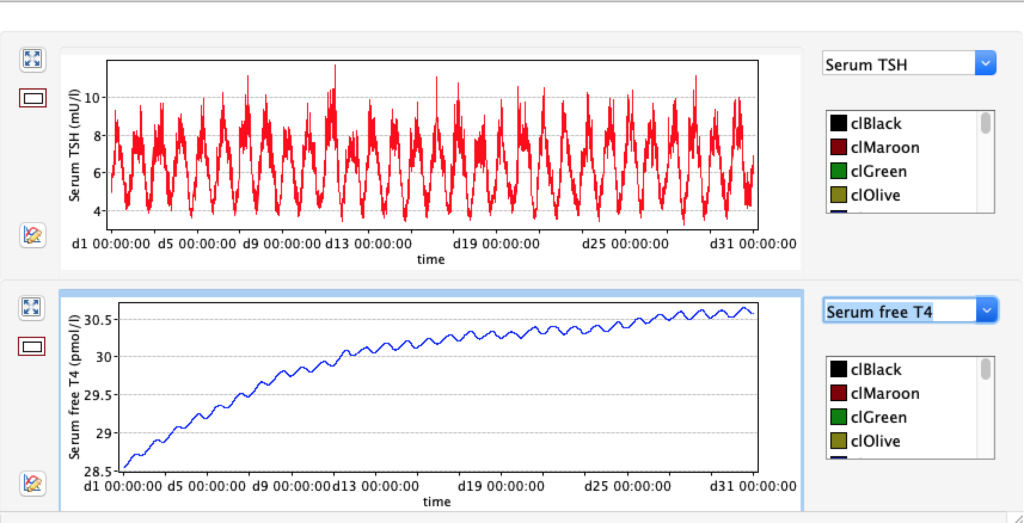
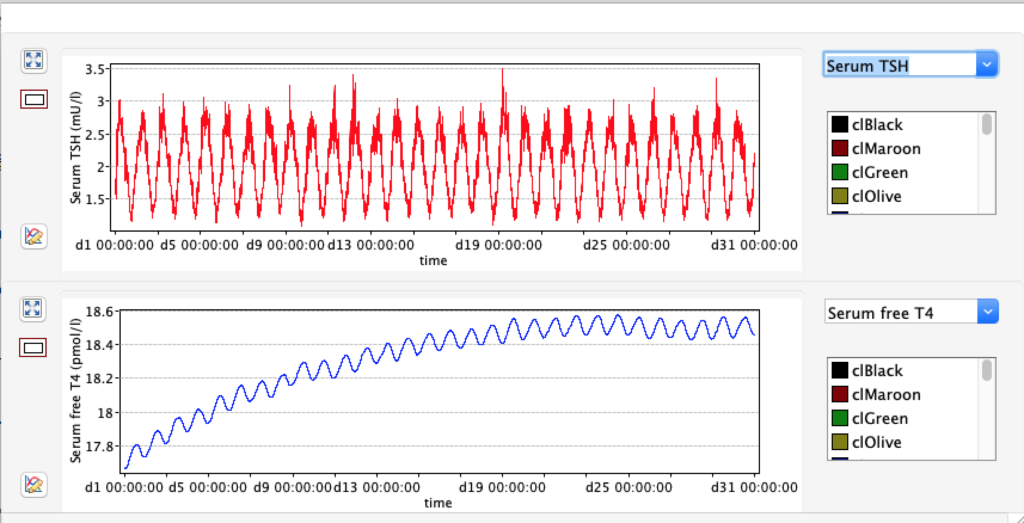
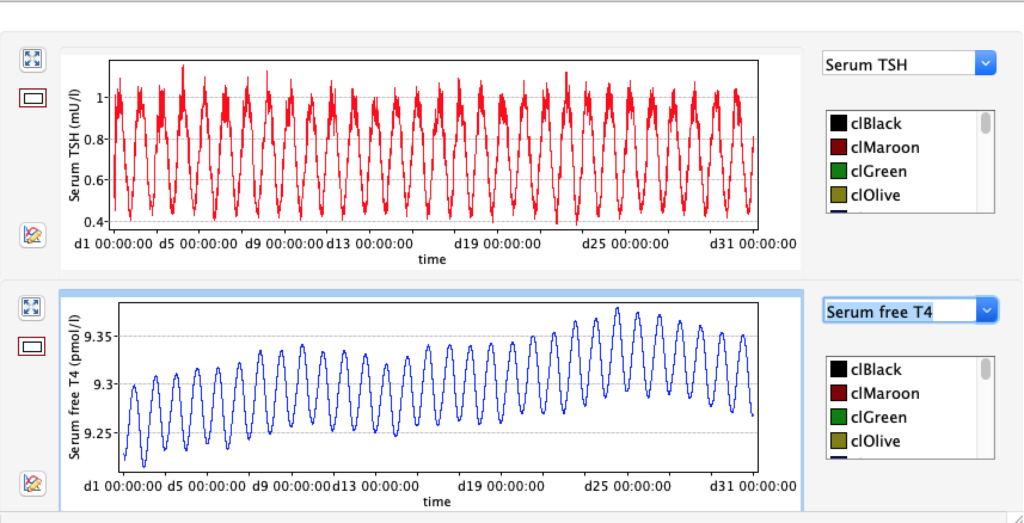
KM 2: dissociation constant of type 2 deiodinase
| TABLE 8.1 | Decrease KM 2 ( /10 ) 1E-10 | STANDARD FIGURES | Increase KM 2 (x10) 1E-8 |
| TRH | 2500 | 2500 | 2500 |
| TSH | 0.7204 | 1,8 | 4.9344 |
| TT4 | 63.6932 | 121,94 | 197.0175 |
| FT4 | 9.2296 | 17,67 | 28.5491 |
| TT3 | 1.6798 | 3,21 | 5.1956 |
| FT3 | 2.7949 | 5,35 | 8.6450 |
| cT3 | 56908.1934 | 11693,7490 | 1917.2921 |
Explain dissociation constants: In chemistry, biochemistry, and pharmacology, a dissociation constant () is a specific type of equilibrium constant that measures the propensity of a larger object to separate (dissociate) reversibly into smaller components, as when a complex falls apart into its component molecules, or when a salt splits up into its component ions. The dissociation constant is the inverse of the association constant. In the special case of salts, the dissociation constant can also be called an ionization constant